Back pain in the area of the shoulder blades is a symptom that is characteristic not only of diseases of the spine, but also of diseases of the internal organs. Why is a doctor's visit necessary and with which specialist should an appointment be made? Effective ways to get rid of ailments.
If you are concerned about back pain in the area of the shoulder blades, such a symptom may indicate diseases of the spine or shoulder girdle, nerve pathologies and somatic diseases. A careful review of the medical history and patient complaints will allow you to identify the cause of the problem and decide on further treatment.
Back pain in the shoulder blade area is often the first signal of pathological changes in the body. And the definition of the provoking factor allows you to early prevent the exacerbation of the disease. The symptom can appear in one half of the body or spread to the arm, appear when inhaling - all these are important for the diagnosis.
The causes of pain and their localization
As a rule, discomfort occurs in the shoulder blade area when moving. For example, a longer static position of the body, an uncomfortable rotation. In this case, pain under the shoulder blade signals damage.
Important!A one-sided pain localization (left under the shoulder blade or right) is rare. This is due to the symmetrical arrangement of the nerve roots of the spinal cord.
Traumatic injury
Painful sensations can indicate muscle or bone damage. In this case, the symptom is diffuse and of varying intensity. The pain is sharp and persists.
Injuries that can cause shoulder blade pain:
- Breaks, cracks. A serious injury where the pain is focused directly on the shoulder blade. The symptom is exacerbated with minimal movement such that the patient cannot move.
- Bruises. The discomfort is superficial, occurs due to damage to the muscle frame and is localized in the lower part of the shoulder blades. The examination can reveal signs of inflammation and tissue swelling. Symptoms last for 14-21 days.
- Subluxation or displacement of the vertebrae. Joint pain occurs below or at the level of the shoulder blades. The symptoms can be aggravated by compressing the nerve roots.
With injuries in the area of damage, soft tissue edema is observed, pain occurs abruptly. There is often a crunch when moving.
Bulging and hernia of the spine
With this pathology, the spinal cord and nerve roots are compressed, which is accompanied by impaired sensitivity and sharp pain under the right and left shoulder blades.
Possible complaints placement:
- Back pain under the shoulder blade on the left or right. Indicates a lesion of 6-12 intervertebral discs with possible involvement of the lumbar spine in the pathological process. Since this is exposed to increased stress, there is a high risk of developing a slipped disc.
- Above the shoulder blades. The protrusion is localized in the cervical spine or in segment 1-3. The symptoms get worse when the head is moved.
- Between the shoulder blades. Pain is observed when 3-6 segments of the spine are affected. It becomes more pronounced with a deep breath that turns the body and pulls the upper limbs to the sides.
Notice!If there is bulging, the pain persists even at rest. This is due to the compression of the nerve roots and muscle spasms.
Osteochondrosis
If the back hurts around the shoulder blades, the symptom may indicate osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine. The symptom occurs due to entrapment of the spinal cord or nerve roots and deformation of the intervertebral disc. The disease progresses gradually, causing more and more vivid symptoms.
The area of discomfort is determined by the location of the lesion:
- 2-6 segments. Complaints are localized at the level of the shoulder blades, radiation of the arm and neck is possible. An increase in intracranial pressure, dizziness from squeezing blood vessels is possible.
- 6-12 segments. There is pain under the shoulder blade on the left or right back and extends to the lower back.
Notice!With osteochondrosis, the pain is one-sided.
Spondyloarthrosis
This pathology is also characterized by unilateral placement of the pain syndrome. Spondyloarthrosis results in a violation of mobility, a feeling of stiffness due to damage to the intervertebral discs and facet joints.
Symptoms depend on the neglect of pathological changes:
- Destruction of cartilage tissue. It develops against the background of decreased blood flow and a violation of the integrity of connective tissue. The cartilage element becomes brittle - quickly damaged and slowly renewed. The situation is made worse by microtraumas due to intense physical exertion. In this case, the pain radiates to the shoulder blades and lower back.
- Deformation of the intervertebral disc. The thickening of the tissue is associated with limited mobility and pain in the shoulder blades and back. Against this background, destructive processes intensify.
- The formation of bone growth. Appear in the advanced form of spondyloarthrosis. They cause damage to blood vessels, muscle tissue, nerves and joints.
In spondyloarthrosis, pain occurs after physical exertion and can be localized in the area of the shoulder blades or between them. The symptom disappears at rest.
Scoliosis
It is accompanied by a transverse curvature of the spine due to the tension in the muscles that support posture. In this case, the spinal cord and nerves are compressed, discomfort under the shoulder blade is observed.
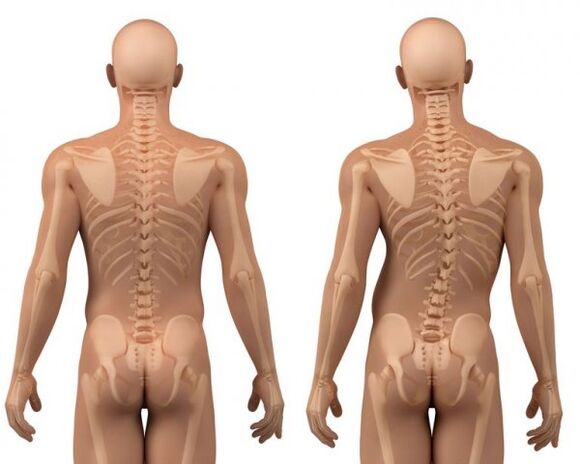
Other symptoms of scoliosis:
- Deformation of the chest. There is a displacement of the ribs and vertebrae, which leads to damage to the spinal cord and its branches. Because of this, back pain is observed on the left under the shoulder blade or on the right.
- Breathing disorder. Due to the deformation of the chest, a dysfunction of the lungs is observed - one of them is compressed, the second tries to make up for the deficit of gas exchange.
- Violation of the activity of the heart. The crooked spine causes shortness of breath, the skin becomes pale, and the heart rate changes.
Notice!Scoliosis is characterized by compression of the spinal cord, so the discomfort is localized between the shoulder blades or below. The pathological focus is clearly defined and can only spread to adjacent areas with muscle spasms.
Kyphosis
Kyphosis is a backward curvature of the spine in which the shoulder girdle is pulled forward, creating a flexion. In this case, the pain is localized above the shoulder blades, is bilateral in nature, radiates to the neck and arm.
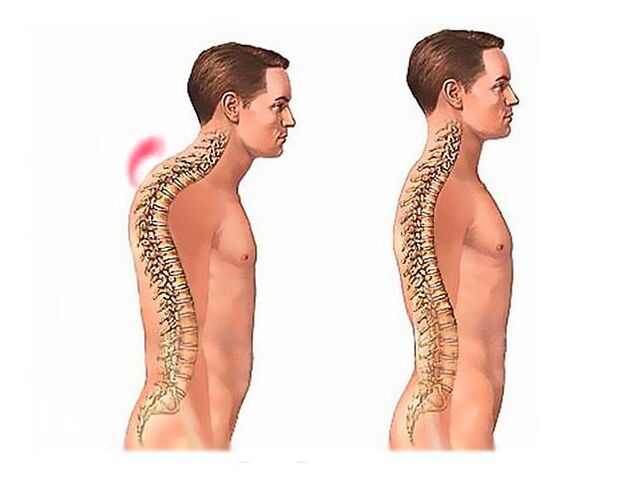
Mechanisms of pain development in kyphosis:
- Muscular. The curvature of the spine leads to overuse of the muscles in the collar area and their cramps, which is accompanied by pain over the shoulder blades.
- Neurogenic. Against the background of the curvature of the spine, the distance between the vertebrae decreases. This leads to an injury to the branches of the spinal cord and the appearance of pain in the area of the shoulder blades, which can spread to the neck, collarbone, shoulder.
With kyphosis, the vertebral artery is compressed, which leads to a deterioration in cerebral blood flow and dysfunction of internal organs.
Radiculitis
The pathology is characterized by pinching of the lumbar roots, which form the sciatic nerve. With the defeat of the upper section, the pain is localized under the shoulder blade and below it. The symptoms are bilateral and get worse with sudden movements.
If left untreated, sciatica is accompanied by other symptoms:
- burning pain in the back (under the shoulder blades and lower back) - indicates pinching of the roots of the spine;
- Lumbago with radiation in the leg;
- Cramps;
- violation of sensitivity in the buttocks, lower back;
- Numbness along the nerve (can be seen on the lower leg, upper leg, foot).
neuralgia
Inflammation of the nerve fibers in this anatomical region can cause pain under the shoulder blades. A common cause of the pathology is hypothermia.

Inflammation can affect structures such as:
- Intercostal nerves. 1-4 pairs along the lower edge of the ribs are affected. The pain is localized under the shoulder blades and, less often, extends to the anterior sections in the lateral parts of the chest.
- Supraspinatus and suprascapular nerves. Characterized by the appearance of pain in the area of the shoulder blades from behind in the area of the collarbone. Sometimes the symptom extends to the shoulders.
- The infraspinatus and subscapularis nerves. Discomfort can be felt under the shoulder blade on the left or right. If the inflammation spreads to the muscles, the pain increases when you move your hands.
Notice!With neuralgia, the pain is often of a one-sided nature - the symptom is localized in the hypothermic part.
Shoulder-scapular periarthrosis
It is characterized by inflammation of the shoulder joint and surrounding tissues. It is associated with restricted mobility, which can only be eliminated after the muscles have warmed up.
In humeroscapular periarthrosis, complaints are observed at the level of the shoulder blades and below. In the initial stage, it appears after intense physical activity, as the disease progresses - at rest. Other symptoms of the pathology:
- Numbness of the upper limbs;
- A headache;
- decreased mobility of the spine.
Cardiac pathology
Pain under the shoulder blades may indicate heart disease. This is because branches of the parasympathetic trunk, connected to the spinal cord and nerve roots, go to the organ. If there is pain under the left shoulder blade from behind, the symptom may indicate a mild form of myocardial infarction. It can last for several days, increase with exercise and decrease at rest.
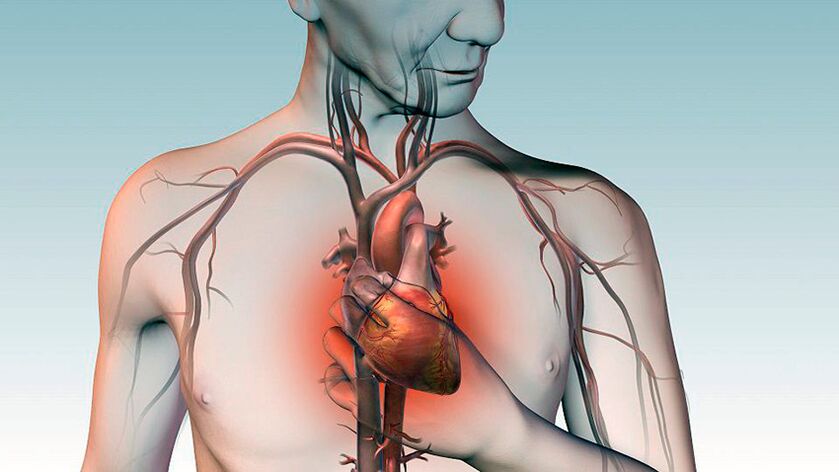
Other signs of pathology:
- burning, pressing pain behind the breastbone;
- Cardiac arrhythmia;
- Palpitations;
- Dyspnea;
- Dizziness;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- increased blood pressure.
Digestive system diseases
The mechanism of onset of pain is similar to the previous reason - distributed along the nerve fibers. The localization of the symptom depends on the organ affected; the symptoms are less common on both sides.
If the back hurts under the shoulder blade on the left, development is possible:
- Inflammation of the lining of the stomach;
- Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas);
- Stomach ulcer.
In addition, with such pathologies there is nausea, vomiting, heartburn, belching and a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen. If the ulcer is complicated by internal bleeding, there will be paleness of the skin, drop in blood pressure, weakness, darkening of the feces.
Discomfort under the right shoulder blade can indicate such discomfort:
- Duodenal ulcer;
- Hepatitis;
- Cirrhosis of the liver;
- Cholelithiasis.
Other causes of the symptom
The following factors can also cause pain in the shoulder blade area:
- Uncomfortable place to sleep. In particular, a folded mattress and sleeping on your left side can cause pain on the opposite side by bending your spine and pinching the roots.
- Vegetovascular dystonia. It is accompanied by a drop in blood pressure, shortness of breath, impaired heart function and sometimes back pain in the shoulder blades.
- Polio. An infectious disease in which shoulder blade pain is neurogenic.
- Pleurisy. With inflammation of the pleura, the symptom occurs due to the friction of their leaves against each other. The peak of the pain occurs with a deep inhalation.
- Kidney pathology. Characterized by aching, stabbing pain under the right shoulder blade. In addition, the color of the urine and the urine output changes.
- Intoxication. Discomfort occurs when an excess of toxins or decay products accumulates in the body against the background of a cold or due to severe poisoning. It is accompanied by chills, muscle pain, fever.
- Subphrenic abscess. When inhaling, pain is observed under the shoulder blades, which is caused by the accumulation of pus in the upper abdominal cavity.
- Mental disorders. Sometimes mental disorders are accompanied by back problems, but the mechanism of their development has not yet been studied.
Types of pain
The type of pain in the shoulder blades area can vary. Depending on this criterion, a possible disease can be assumed and the cause of the symptoms can be determined:
- Shooting, sharp, arising from turning the body or moving. Typical for pinched nerves. This feature makes it possible to distinguish it from pain in gallstone disease - with this diagnosis, the discomfort is constant and does not depend on movements.
- Cutting, boring pain of varying intensity. May indicate neuralgia, inflammation of the joints.
- Throbbing, pain, or burning. Such pain in the area of the shoulder blades indicates diseases of the internal organs. The symptom develops due to compression of the nerve roots, with movement it can become more pronounced.
- Choking pain at or below shoulder blades. Typical of a hernia of the spine. Often accompanied by numbness of the arms or legs, lumbago.
Which doctor should I go to?
If there are painful sensations in the area of the shoulder blades, you should make an appointment with a neurologist. The doctor conducts an examination, makes a diagnosis and determines the tactics of treatment. In case of detection of pathologies of the internal organs, he will refer to a specialist with a narrow profile - a gastroenterologist, cardiologist, orthopedic surgeon (depending on the alleged diagnosis).
survey
To determine the cause of the appearance of pain in the area of the shoulder blades, the following diagnostic procedures are assigned to patients:
- Clinical studies of blood, urine. They show inflammatory changes, help diagnose somatic diseases.
- X-ray examination, CT. They allow you to identify curvatures of the spine, injuries and their consequences, osteochondrosis.
- Ultrasonic. It is used to identify pathologies of internal organs.
- EKG. Informative if heart disease is suspected.
- MRI. Reflects the state of the spine, shoulder girdle and internal organs. The examination area is determined by the doctor depending on the proposed diagnosis.
Notice!Pain below the shoulder blades is often indicative of neurological abnormalities. Therefore, CT and MRI are the "gold standard" in determining the cause of a symptom.
Treatment features
The goal of treatment is not only to get rid of pain, but also to get rid of the factor that led to its appearance. When looking for medical help, the pain syndrome is alleviated and an etiological treatment to eliminate the underlying disease is agreed.
The therapeutic program can include the following methods:
- Medical treatment. To relieve pain, drugs from a range of analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs are used. Depending on the cause of the symptom, antibacterial agents, diuretics, gastroprotectors, etc. can be used.
- Physical therapy. Helps accelerate recovery from somatic pathologies and strengthen the spine. To get rid of pain in the area of the shoulder blades, electrophoresis, UHT, and heating methods are used.
- Massage. Helps remove muscle spasms, improve posture, relieve painful sensations. It is prescribed for problems with the spine. Sometimes the intervention of an osteopath or chiropractor is required.
- Gymnastics. Displayed during the recovery phase. Depending on the established diagnosis, a number of exercises are selected individually for each patient.
How can you prevent discomfort in the shoulder blade area?
Any patient who has undergone treatment is then advised to take a number of preventive measures. They are necessary to prevent the disease from recurring.
It is important to follow these rules:
- create favorable sleeping conditions - choose an orthopedic pillow and mattress of moderate firmness to support the physiological position of the spine;
- pay attention to your posture;
- follow the principles of proper nutrition;
- try to prevent exacerbation of chronic pathologies;
- Giving up addictions (smoking, drinking alcohol);
- Visit your doctor regularly for checkups.
Pain in the shoulder blades can have somatic and neurological causes. In the latter case, the symptom appears sharp and is pronounced. With somatic origin, the pain grows gradually and lasts for a long time, does not depend on body movements.
Analgesics can be used to relieve an uncomfortable symptom. However, in order to completely eliminate pain sensations, it is important to undergo full treatment aimed at getting rid of the underlying pathology. Only a doctor, after a full examination, can develop the correct course of therapy.





































